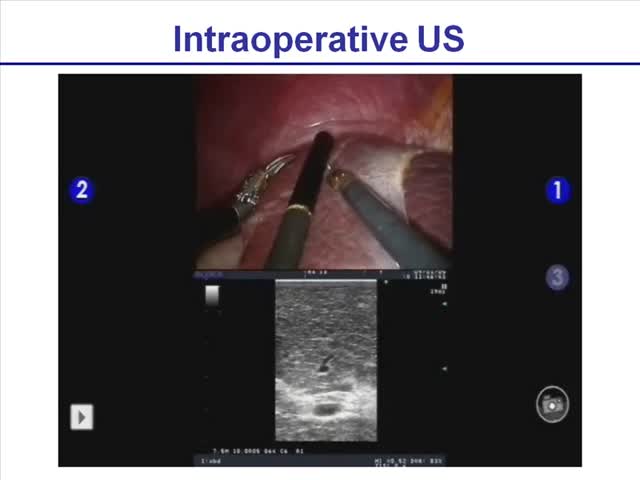
Chicago 2009 Video – Da Vinci Robot-Assisted Left Hepatectomy
January 13, 2010
G.H. Choi
Background
Since the minimally invasive surgery has been developed in all surgical fields, laparoscopic liver resection has been more frequently performed by many surgeons. However, laparoscopy has the limitations such as 2-dimensional imaging and restricted instrument motion. The da Vinci Robotic system provides 3-dimensional images and EndoWrist with a 360-degree range of motion.
Methods
From January 2009, four patients underwent robotic assisted left hepatectomy in Yonsei University Health System, Seoul, Korea. The patient is placed in a supine position with reverse Trendelenburg(15°). We use 5 ports altogether; 4 for the robotic arms and 1 for the assistant surgeon. The camera port is placed just below the umbilicus. Three 8-mm robotic ports are introduced in the both sub-costal areas along the midclavicular line and the left flank area, respectively. The assistant port (12mm) is placed in the right para-umbilical area, 5cm apart from the umbilicus. In recent two cases, two 2mm trocars were used to retract both the liver edges by rubber bands, which facilitated full and constant exposure of dissected area during the parenchymal transaction. The specimen was pulled out through either the supra-pubic incision or previous incision.
Results
Four patients (1 hepatocellular carcinoma, 2 cholangiocellullar carcinomas and 1 liver metastasis from the rectal cancer) underwent robotic assisted left hepatectomy. The average operating time was 560 minutes (range: 460- 670). The average estimated blood loss was 497 cc (range: 200-900). The second case was converted to the mini-laparotomy due to the uncontrolled bleeding during the parenchymal transaction. This patient developed wound infection. There was no complication in three other patients. The mean days of hospitalization were 12 (range: 7-22).
Conclusions
In our limited experience, robotic assisted left hepatectomy seems to be a feasible and safe procedure, and further experience should be needed to standardize the surgical technique.