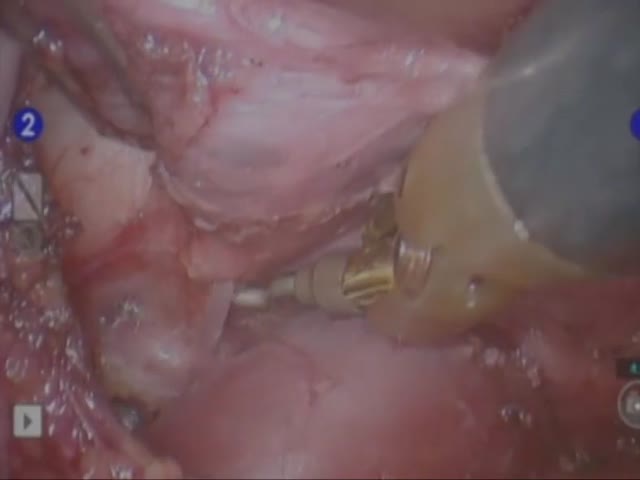
Chicago 2009 Video – Right Thorascopic Approach for Robot-Assisted Thymectomy in Patient whit Myasthemia Gravis
January 20, 2010
F. Sbrana
Background/Hypothesis
The approach to the mediastinal space represents one of the most interesting applications of the Da Vinci Robotic system allowing a precise dissection in narrow anatomical regions. Different video–assisted approaches (left-side, right-sided, bilateral or subxifoid) have been described for this operation. In this video we report the technique for robotic thymectomy by a right thoracoscopic approach underlining the potential advantage of a closer control of the anonimus-cava confluence.
Materials & Methods
Standard patient positioning is a partial left lateral decubitus (30 degrees). Four trocars are used. The port for the robotic endoscope is positioned in the fifth intercostal space in the middle axillary line. The two robotic instruments are placed on the third intercostal space on the posterior axillary line and on the sixth intercostal space on the anterior axillary. The dissection is begun opening the triangle between the right phrenic nerve and the internal mammary vessels. The right approach is offering the complete visual control of the superior vena cava and the confluence of the anonimus vein. The dissection of the right upper corner of the thymus is made easier and safer from this side.
Results
From November 2008 to July 2009 a right approach for robotic thymectomy has been applied in four consecutive patients. There were three man and one woman with a mean age of 52.5 years( range, 55-80 years). All patients had preoperative diagnosis of myasthenia gravis. All procedures have been successfully completed robotically with a mean operative time of 140 minutes (range 120-180 min). Blood loss was negligible in all cases. Mean postoperative length of stay was 2.5 days(ange 2-3). No postoperative morbidity was observed. Histhologic examination revealed one thymic hyperplasia and three thymoma.
Conclusions
Robot-assisted thymectomy from right single-sided approach is a feasible, safe and reproducible technique. It allows a complete dissection of upper thymic horns, control of thymic vein and provides an excellent access to the anterior mediastinum.. The minimally invasive thymectomy guarantees decrease postoperative pain, better preservation of respiratory function, improved cosmesis and faster recovery.