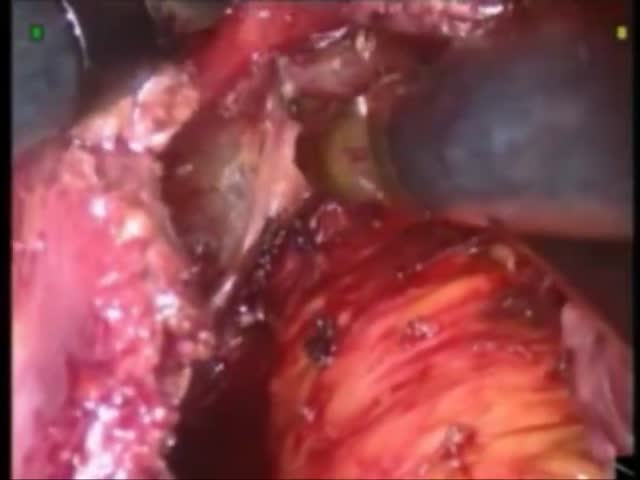
Chicago 2009 Video – Laparoscopic robot-assisted transhitial esophagectomy
December 22, 2009
R. Pugliese , D. Maggioni, GC. Ferrari, A. Forgione, C. Magistro, M.Gualtierotti
SUMMARY
This video shows the feasibility of robot-assisted transhiatal esophagectomy. The long EndoWrist instruments allow a precise dissection of the esophagus from the right and left crus with an easy access to the mediastinum avoiding pleura opening. Transhiatal dissection of the esophagus is continued in a cephaled direction proximal to carina. The left gastric artery and vein are isolated and transacted between clips. The gastric conduit, created along the lesser curvature ,using stapler device, is pulled up into the mediastinum and out through the cervical incision where gastroesophageal anastomosis is performed. Robotic assistance overcoming traditional pitfalls of laparoscopy, increase the surgeon’s ability to work in the narrow space of the mediastinum
Background
Minimally invasive esophagectomy is a technically demanding procedure. Robotic technology can help the surgeon in this field. This video shows a robot assisted transhiatal esophagectomy.
Patients and methods
Patient under general anesthesia with legs divided in reverse Trendelenburg. The first part of the operation: gastrocolic opening, short gastric vessels transection with preservation of gastroepiploic ones is performed by laparoscopy. Then the da Vinci® Robotic Surgical System is brought cephalad to the patient. The gastrohepatic ligament is opened. The right crus is mobilized from the phrenoesophageal membrane. Blunt dissection is performed to separate the esophagus from the left crus and a retroesophageal window is created. Transhiatal dissection of the esophagus is continued in a cephaled direction proximal to carina. The left gastric artery and vein are isolated and transacted between clips. Mobilization of the proximal esophagus along the mediastinum is completed by a cervical access. The gastric conduit, created along the lesser curvature using stapler device, is pulled up into the mediastinum and out through the cervical incision where gastroesophageal anastomosis is performed
Results
No intraoperative complication was registered. The operating time was 320 minutes, the set up of robot was 20 minutes. The post-operative course was uneventful.
Conclusions
This video shows the feasibility of robot-assisted transhiatal esophagectomy. The long EndoWrist instruments allow a precise dissection of the esophagus with an easy access to the mediastinum avoiding pleura opening. Robotic assistance overcoming traditional pitfalls of laparoscopy like straight and shorts instruments, two dimensional imaging and poor ergonomics increase the surgeon’s ability to work in the narrow space of the mediastinum.